The lamination of a bush also helps to decrease the work rate of the elastomer under high radial loads.
Laminated bushes
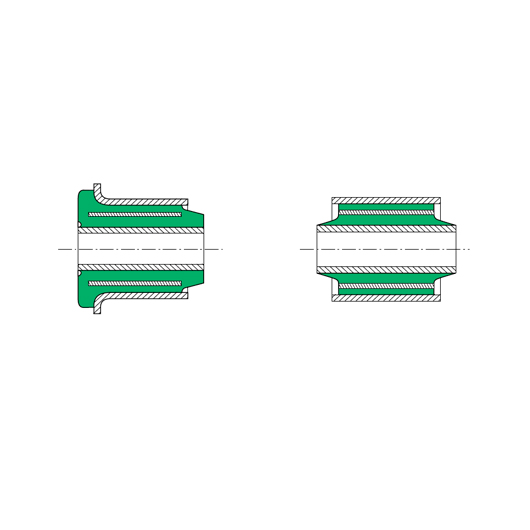
This type of bush has a thin metallic tube between the internal tube and the external tube.
The object is to have a higher stiffness radially while keeping practically the same stiffness in torsion.
Download PDF catalog
Related products
In this type of bush, one of the tubes is flanged.
Download PDF catalog
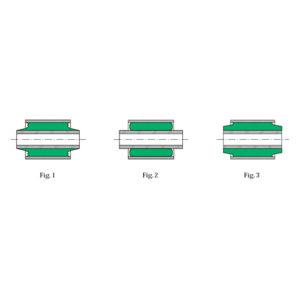
FLEXIBLOC (fig. 1) – FULLY BONDED
This is a bush made up of 2 concentric tubes between which of elastomer is bonded. Under the effect of external forces or torques, the relative movement of the tubes will cause an elastic deformation of the elastomer. By consulting the service conditions, a bush should be chosen which will remain within its elastic operational limits.
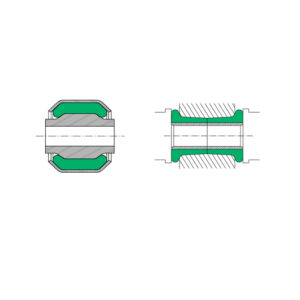
SILENTBLOC (fig. 2) – PRESTRESSED
This is a bush made up of 2 concentric tubes between which a ring of “adhérite®” elastomer is inserted by force. Under the effect of external forces or torques, the relative movement of the tubes will cause an elastic deformation of the elastomer. Above a certain value the adherite will slide in the tubes.
Download PDF catalog
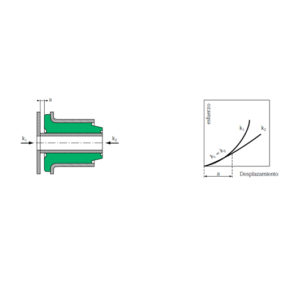
A void bush is designed to have radial stiffness which are very different at 90° to each other.
Download PDF catalog
“PRESTRESSED BUSHES” with turned down sides:
For the same dimensions, this type of bush provides a radial load capacity which is superior to that of the classic “prestressed”.
In addition, versions of relatively short length permit conical movement more easily (reduced torque and increased angle).
CONICAL BUSH:
This takes the form of a rubber sleeve whose external surface is a truncated, and which surrounds a cylindrical internal part to which it adheres strongly by high radial expansion.
Assembly in pairs, in a housing made up of two truncated cones placed small end to small end.
By axial pressure, a high compression is created which ensures the external adherence of the rubber and causes lateral cushions to form at each end of the housing. These cushions ensure resistance to axial forces.